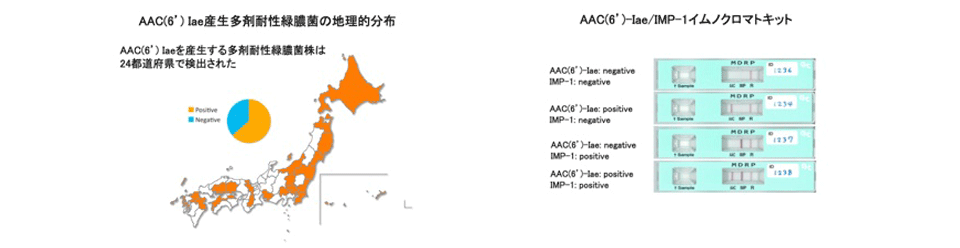
Epidemiological studies of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and development of rapid diagnostic kits
The emergence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains resistant to carbapenems, fluoroquinolones and amikacin, which are defined as multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains, is a serious problem in Japan and other Asian countries. Nosocomial outbreaks of MDR P. aeruginosa infections in hospitals are increasing, with 2.5% of P. aeruginosa isolates at medical facilities being MDR. Furthermore, clonal expansion of P. aeruginosa strains highly resistant to these antibiotics, with MICs over 64 μg/ml, has been observed in community hospitals. Most of these strains were found to produce metallo-β-lactamase IMP-1 and aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase AAC(6')-Iae. We performed several epidemiological studies of MDR P. aeruginosa in Japan and other Asian countries, including Vietnam and Nepal. We also developed immunochromatographic assays for the rapid detection of these enzymes-producing strains. These assays are easy to use and reliable in detecting MDR P. aeruginosa.
Selected Publications
- Oshiro S 2015 in J Microbiol Methods. 118: 159-163
- Tada T 2014 in BMC Infectious Diseases 14:56
- Tada T 2014 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58 (6) p3538-3540
- Tada T 2014 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58 (5) p2916-2920
- Tada T 2013 in International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 42 (4) p372-324
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (9) p4427-4432
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (5) p2394-2396
- Tada T 2013 in BMC Infectious Diseases 13(1) 251
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (1) p96-100
- Tada T 2012 in Journal of Microbiological Methods 91 (1) p114-116
- Kitao T 2012 in International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 39 (6) p518-521
- Kitao T 2011 in Journal of Microbiological Methods 87 (3) p330-337
- Kitao T 2010 in Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 65 (7) p1382-1386
- Sekiguchi J 2005 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 49 (9) p3734-3742
Development of rapid diagnostic kits for drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis and elucidation of their molecular resistance mechanisms to antituberculosis drugs
We developed a new line probe assay (LiPA) kit to identify Mycobacterium species and to detect mutations related to drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A total of 554 clinical isolates of Mycobacterium species, including 316 M. tuberculosis isolates, from six hospitals were assayed with the LiPA kit. The LiPA kit was also used to directly test 163 sputum specimens. The results using the LiPA kits in identifying Mycobacterium species in clinical isolates were almost identical to those of conventional methods. Compared with standard drug susceptibility testing results for these isolates, LiPA showed a sensitivity of 98.9% and a specificity of 97.3%. These kits were able to identify mycobacterial bacilli, including drug-resistant phenotypes, at the species level, with high sensitivity and specificity.
Drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is caused by mutations in restricted regions of the genome. Mutations in katG, the promoter region of the mabA-inhA operon, and inhA are those most frequently responsible for isoniazid (INH) resistance. Several INH-resistant (INHr) Mtb clinical isolates without mutations in these regions have been described, however, indicating that there are as yet undetermined mechanisms of INH resistance. We found that a significant number of INHr Mtb clinical isolates without known INH resistance mutations contained the mabAg609a silent mutation and showed that this mutation resulted in the upregulation of inhA, a gene encoding a target for INH, converting the region adjacent to the mutation into an alternative promoter for inhA. The mabAg609a silent mutation results in a novel mechanism of INH resistance, filling in a missing piece of INH resistance in Mtb.

Selected Publications
- Ando H 2014 in Molecular Microbiology 91 (3) p538-547
- Ando H 2011 in Molecular Microbiology 79 (6) p1615-1628
- Ando H 2011 in Journal of Medical Microbiology 60 (2) p184-188
- Ando H 2010 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 54 (5) p1793-1799
- Ando H 2009 in Clinical Microbiology and Infection 16 (8) p1164-1168
- Sekiguchi J 2007 in Journal of Clinical Microbiology 45 (9) p2802-2807
- Sekiguchi J 2007 in Journal of Clinical Microbiology 45 (1) p179-192
Development of rapid diagnostic kits for detection of highly pathogenic avian H5N1 influenza in humans
We developed kits for the rapid diagnosis of the highly pathogenic avian H5N1 influenza in humans. This kit, using immunochromatography, is simple to use and can markedly shorten sharply the assay time, from 6 hours to 15 min.
Selected Publications
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Journal of Virological Methods 185 (2) p276-280
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses 6 (6) p434-441
- Kawachi S 2011 in Journal of Clinical Virology 51 (1) p68-72
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2010 in Journal of Clinical Microbiology 48 (3) p703-708
Molecular mechanisms of severe invasive streptococcal infection
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE) causes invasive streptococcal infections, including streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS), as does Lancefield group A Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS). Recent epidemiological studies showed that the incidence of invasive SDSE infections has been increasing in Asia, Europe, and the United States. We sequenced the entire genomes of Lancefield group G SDSE strain GGS_124 and Lancefield group C SDSE strain 167 isolated from a patient with STSS.
We also analyzed the SDSE transcriptome in vivo during intraperitoneal infection in mice. Microarray data suggest that SDSE degrades host tissue polysaccharides by secreting poly/oligosaccharide lyases, as well as simultaneously using the Entner-Doudoroff pathway to metabolize acquired carbohydrates. Our findings suggest that the concomitant regulation of virulence factors that destroy host tissues and metabolic enzymes may play an important role in invasive diseases induced by SDSE.
Selected Publications
- Ogura K in 2017 J Genomics. 5:71-74
- Watanabe S 2016 in Microbiol and Immunol 60(1) p1-9
- Watanabe S 2013 in Genome Biology and Evolution 5 (9) p1644-1651
- Watanabe S 2013 in Journal of Infectious Diseases 208 (9) p1482-1493
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Journal of Bacteriology 194 (19) p5466
- Okumura K 2012 in BMC Genomics 13, 404
- Shimomura Y 2011 in BMC Genomics 12, 17
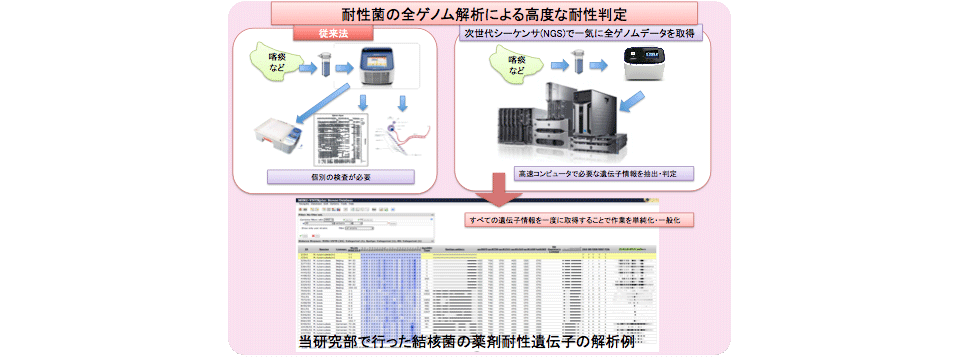
Epidemiological studies based on complete genome information
We performed epidemiological studies of infectious diseases by whole bacterial genome sequence analysis.
Selected Publications
- Tada T 2017 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. pii: AAC.01806-17.
- Uechi K 2017 in J Infect Chemother. pii: S1341-321X(17)30208-8
- Shrestha B 2017 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. pii: AAC.01425-17
- Tada T 2017 in BMC Infect Dis.17(1):467
- Tada T 2017 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 61(9). pii: e00694-17.
- Tada T 2017 in Int J Infect Dis. 63:72-73
- Tada T 2017 in Int J Infect Dis.63:21-22.
- Ogura K 2017 in J Genomics. 2017 5:71-74
- Tada T 2017 in BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 4;17(1):467
- Tada T 2017 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 61(3). pii: e02300-16.
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2016 in mSphere. 1(5). pii: e00289-16
- Hayakawa K 2016 in American Journal of Infection Control. 44(11):e257-e259.
- Tada T 2016 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 60(11):6853-6858
- Shrestha S 2016 in J Nepal Health Res Counc.14(33):72-76
- Watanabe S 2016 in Microbiol and Immunol 60(1):1-9
- Tada T 2016 in PLoS One 11(4):e0149385
- Matono T 2016 in BMC Res Notes 9(1):197
- Oshiro S 2015 in J Microbiol Methods. 118: 159-163
- Shrestha B, Tada T 2015 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 59(9): 5847-5850
- Iwai H 2015 in Tuberculosis 95 (6) p843-844
- Tada T 2015 in BMC Infect Dis 15:433
- Shrestha B 2015 in JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 53(198) p89-95
- Tada T 2015 in Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59 (11) p7090-7093
- Shrestha S 2015 in Int J Antimicrob Agents 46(5) p 526-531
- Tada T 2015 in Microb Drug Resist 22(2) p103-108
- Nhung PH 2015 in J Infect Chemother 21(8) p 617-619
- Iwai H 2015 in Tuberculosis 95(3)p246-250
- Sherchan JB 2015 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2015 Mar 30. [Epub ahead of print]
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2015 in Tuberculosis 95(1): 37-39
- Okumura K 2015 in BMC Genomics 16(1): 218
- Kato-Miyazawa M 2015 in Clinical Microbiology and Infection 21(3): 248.e1-248.e8.
- Tojo M 2015 in Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy 21(3): 212-214.
- Tada T 2014 in BMC Infectious Diseases 14:56
- Tada T 2014 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58 (6) p3538-3540
- Hayakawa K 2014 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58(6) p3441-3450
- Tada T 2014 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 58 (5) p2916-2920
- Ando H 2014 in Molecular Microbiology 91 (3) p538-547
- Arai R 2014 in BJournal of Veterinary Medical Science 76(6) p491-498
- Tada T 2013 in International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 42 (4) p372-324
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (9) p4427-4432
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (5) p2394-2396
- Tada T 2013 in BMC Infectious Diseases 13(1) 251
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2013 inPLoS ONE 8(6): e66358
- Tada T 2013 in Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 57 (1) p96-100
- Watanabe S 2013 in Genome Biology and Evolution 5 (9) p1644-1651
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Journal of Bacteriology 194 (20) p5692
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Journal of Bacteriology 194 (19) p5466
- Okumura K 2012 in BMC Genomics 13, 404
- Okumura K 2012 in Journal of Bacteriology 194 (11) p3014
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2012 in Journal of Bacteriology 194 (10) p2770
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2011 in Journal of Bacteriology 193 (24) p7010
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2011 in Journal of Bacteriology 193 (23) p6792
- Tada T 2011 in Journal of Bacteriology 193 (22) p6397
- Okumura K 2011 in Journal of Bacteriology 193 (15) p4029-4030
- Shimomura Y 2011 in BMC Genomics 12, 17
Development of Tuberculosis-sensitive mice
Selected Publications
- Iwai H 2015 in Tuberculosis 2015 Mar 21. [Epub ahead of print]
- Miyoshi-Akiyama T 2015 in Tuberculosis 95(1): 37-39
